Types of Diseases
- Skin Problems
- Spinal Problems
- Infertility Problems
- Anorectal Problems
- Joint Problems
- Gastrointestinal Problems
- Paediatric Problems
01.
Skin Problems
1.Psoriasis
2.Eczema
3.Vititiligo
4.Lichenplanus

1.Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin. The extra skin cells form scales and red patches that are sometimes itchy and painful. Psoriasis is a common condition that affects people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 15 and 35.
Ayurveda is a traditional system of medicine that originated in India. It aims to treat the root cause of a disease rather than just the symptoms. In Ayurveda, Psoriasis is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the three doshas (energies that govern the body), which leads to the accumulation of toxins (ama) in the body. The treatment of Psoriasis in Ayurveda involves balancing the doshas, eliminating toxins from the body, and restoring the body’s natural equilibrium.
2.Eczema
Eczema is a term for a group of skin conditions that cause inflammation of the skin. It is also known as dermatitis. Eczema can cause dry, red, and itchy skin, and in some cases, blisters and sores. The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an immune system dysfunction and a genetic predisposition.
Eczema may be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics
- Allergens such as pollens, mold, and animal dander
- Infections
- Stress
- Changes in temperature and humidity
- Hormonal changes
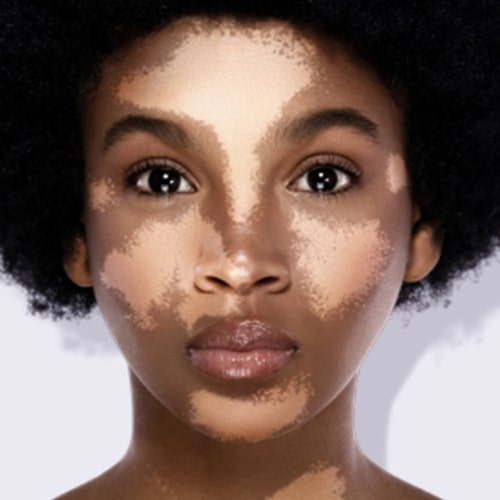
3.Vititiligo
Vitiligo is a condition in which the skin loses its pigment cells. This can cause white patches to appear on the skin, and can also affect the hair and mucous membranes. The cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys the pigment cells. Other factors that may contribute to the development of vitiligo include genetics, sunburn, and certain medications.
In Ayurveda, vitiligo is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for vitiligo typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.
Some Ayurvedic remedies for vitiligo may include:
- Guggulu, a herb that has immune-modulating and antioxidant properties
- Bhrungaraj, an herb that has been traditionally used to treat skin disorders
- Turmeric, which has anti-inflammatory properties and may help to stimulate pigment production
- Amalaki, a fruit that has antioxidant properties and may help to support healthy skin function

2.Lichenplanus
Lichen planus is a condition that causes a rash or bumps on the skin or mucous membranes. The rash is typically purple or red and may be itchy. It can occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the wrists, ankles, and lower back. The cause of lichen planus is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an immune system dysfunction. Other factors that may contribute to the development of lichen planus include certain medications, infections, and exposure to certain chemicals.
In Ayurveda, lichen planus is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for lichen planus typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.
Some Ayurvedic remedies for lichen planus may include:
- Turmeric, which has anti-inflammatory properties
- Neem, an herb that has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties
- Guggulu, a herb that has immune-modulating and antioxidant properties
- Bhrungaraj, an herb that has been traditionally used to treat skin disorders

02.
Spinal Problems
1.Neck Pain
2.Lowback Pain
3.Cervical spondylitis
4.Lumbar spondylitis

1.Neck Pain
Neck pain is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. It can be acute, meaning that it comes on suddenly and lasts for a short period of time, or chronic, meaning that it persists for a longer period of time. Neck pain can be caused by muscle strain, poor posture, injuries, and degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis. It can also be a result of tension headaches, which are caused by muscle tension in the neck and head.
In Ayurveda, neck pain is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for neck pain typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.
2.Low Back Pain
Low back pain is a common condition that affects the lower part of the spine. It can be acute, meaning that it comes on suddenly and lasts for a short period of time, or chronic, meaning that it persists for a longer period of time. Low back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, poor posture, injuries, and degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis. It can also be a result of underlying conditions such as kidney infections or spinal stenosis.
In Ayurveda, low back pain is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for low back pain typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.

3.Cervical Spondylitis
Cervical spondylitis, also known as cervical osteoarthritis or cervical spondylosis, is a condition that affects the neck region of the spine. It is caused by the gradual wear and tear of the bones and cartilage in the neck over time. It is more common in people who are older and in those who have a history of neck injuries. Cervical spondylitis can cause neck pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the neck. In severe cases, it can cause numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms and hands.
In Ayurveda, cervical spondylitis is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for cervical spondylitis typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.
4.Lumbar Spondylitis
Lumbar spondylitis, also known as lumbar osteoarthritis or lumbar spondylosis, is a condition that affects the lower part of the spine, specifically the lumbar region. It is caused by the gradual wear and tear of the bones and cartilage in the lower back over time. It is more common in people who are older and in those who have a history of lower back injuries. Lumbar spondylitis can cause low back pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the lower back. In severe cases, it can cause numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs.
In Ayurveda, lumbar spondylitis is thought to be caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas, or energy centers. Ayurvedic treatment for lumbar spondylitis typically involves a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying imbalances and bring the body back into balance.
03.
Joint Pains
1.Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.Osteo Arthritis

1.Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints and surrounding tissue. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to inflammation, pain, and damage in the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect other organs in the body, such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to develop the disease, and certain environmental factors, such as tobacco smoke and exposure to certain viruses and bacteria, may increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
2.Osteo Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of joint disease that results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It is the most common type of arthritis, and it typically affects the joints in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
OA is often caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, although other factors such as genetics, obesity, and previous joint injuries can also contribute to the development of OA.
In Ayurveda, OA is considered to be caused by an imbalance of the doshas (bodily humors) and an accumulation of ama (toxins) in the body. Treatment for OA in Ayurveda may include dietary changes, herbal remedies, massages, and yoga or other exercises to strengthen the affected joints. It is important to consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for personalized treatment recommendations.
04.
Gastrointestinal Problems
1.Hyperacidity
2.Indigestion
3.Constipation
4.Loss of Appetite
ETC

1.Hyperacidity
Hyperacidity, also known as acid reflux or heartburn, is a condition in which there is an excess production of acid in the stomach. This excess acid can cause irritation and inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, belching, and nausea.
Hyperacidity can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Eating a diet that is high in acidic foods, such as citrus fruits, tomato-based products, and spicy foods.
- Consuming large amounts of alcohol or caffeine.
- Overeating or eating too quickly.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin.
- Stress and anxiety.
- Hiatal hernia, in which part of the stomach protrudes into the chest through a hole in the diaphragm.
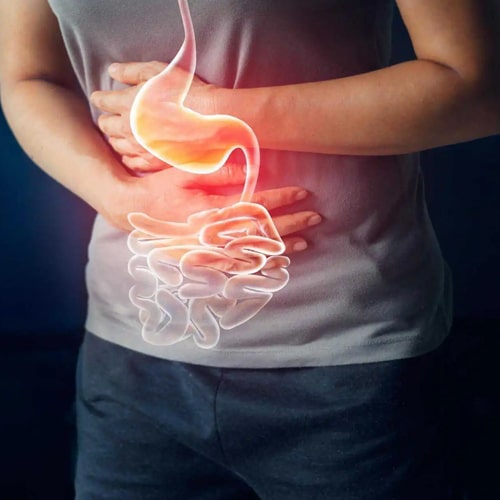
2.Indigestion
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of joint disease that results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It is the most common type of arthritis, and it typically affects the joints in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
OA is often caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, although other factors such as genetics, obesity, and previous joint injuries can also contribute to the development of OA.
In Ayurveda, OA is considered to be caused by an imbalance of the doshas (bodily humors) and an accumulation of ama (toxins) in the body. Treatment for OA in Ayurveda may include dietary changes, herbal remedies, massages, and yoga or other exercises to strengthen the affected joints. It is important to consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for personalized treatment recommendations.
3.Constipation
Constipation is a condition in which a person has difficulty passing stools or has infrequent bowel movements. It is often characterized by hard, dry stools that are difficult to pass.
There are many potential causes of constipation, including:
- A diet low in fiber and fluids
- Lack of physical activity
- Certain medications, such as painkillers and antidepressants
- Hormonal imbalances
- Changes in routine or lifestyle
- Aging
- An underlying medical condition, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
4.Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite is a decrease in the desire to eat and can be caused by a variety of physical and psychological factors. Physical causes of loss of appetite can include illness, infection, digestive issues, and certain medications. Psychological causes can include stress, anxiety, and depression.
In Ayurveda, loss of appetite is often considered to be caused by an imbalance in the doshas, or the three energies that govern the body. In particular, an imbalance in the Kapha dosha is often associated with loss of appetite.
To treat loss of appetite in Ayurveda, a person may be recommended to follow a specific diet and lifestyle, as well as to take herbal remedies and other natural substances to restore balance to the doshas.

05.
Infertility Problems
1.Male – Low spermcount
2.Premature Ejaculation
3.Erectile Disfunction
4.Female – Hormonal Problems
5.PCOD
ETC

1.Male – Low sperm count
Male low sperm count, also known as oligozoospermia, is a condition in which a man has a lower than normal number of sperm in his ejaculate. A normal sperm count is considered to be at least 15 million sperm per millilitre of semen. A sperm count below this level may make it more difficult for a man to father a child.
There are many potential causes of low sperm count. Some common causes include:
- Varicocele: This is a condition in which the veins in the testicle are enlarged, which can cause the testicle to become overheated and damage sperm production.
- Infection: Infections of the reproductive system, such as chlamydia or gonorrhoea, can cause inflammation and damage the testicles, leading to low sperm count.
- Hormonal imbalances: Abnormal levels of hormones such as testosterone or prolactin can interfere with normal sperm production.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, such as pesticides or heavy metals, can affect sperm production.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome, can cause low sperm count.
- Lifestyle factors: Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use, can also affect sperm production.
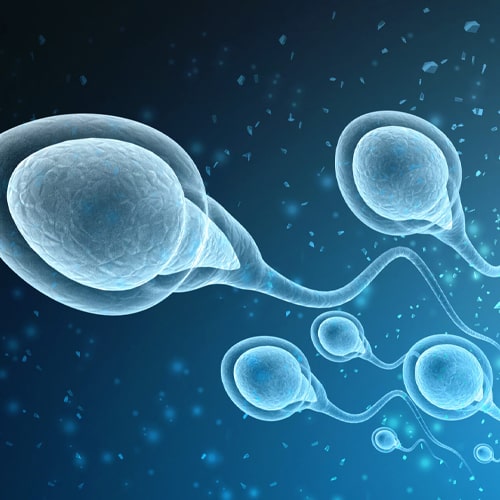
2.Premature Ejaculation
Premature ejaculation (PE) is a condition in which a man ejaculates sooner during sexual intercourse than he or his partner would like. It can be a frustrating and embarrassing problem, and it can cause significant stress and relationship difficulties if not addressed.
There are several potential causes of premature ejaculation, including:
- Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can all contribute to premature ejaculation. Past sexual experiences, including trauma or abuse, may also play a role.
- Physical factors: Certain medical conditions, such as prostate problems or hormonal imbalances, can cause premature ejaculation. In addition, certain medications, such as antidepressants, can affect ejaculation.
- Lifestyle factors: Alcohol and drug use, as well as certain lifestyle habits, can contribute to premature ejaculation.
In Ayurveda, premature ejaculation is often considered a result of an imbalance in the doshas, particularly an excess of vata and a deficiency of pitta. Ayurvedic treatment for premature ejaculation may include herbal remedies, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications, such as practising yoga and meditation. Some specific herbs that may be helpful include ashwagandha, shatavari, and gokshura. It is important to consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for personalised treatment recommendations.

3.Erectile Disfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition in which a man is unable to get or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It is also sometimes referred to as impotence.
There are many potential causes of ED, including physical and psychological factors. Physical causes may include conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, and low testosterone. Psychological causes may include stress, anxiety, and depression. In some cases, ED may be a side effect of certain medications.
In Ayurveda, ED is considered to be a result of an imbalance in the doshas, particularly the vata and kapha doshas. Ayurvedic treatment for ED typically involves a combination of herbal remedies, diet and lifestyle changes, and treatments such as massage and yoga.
Herbal remedies that may be used to treat ED in Ayurveda include ashwagandha, shatavari, and ginkgo biloba. These herbs are believed to support overall health and well-being, as well as improve circulation and increase libido.
Diet and lifestyle changes that may be recommended include following a healthy, balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress through techniques such as meditation and deep breathing.

4.Female – Hormonal Problems
Female hormonal problems refer to imbalances or abnormalities in the hormones produced by the female reproductive system. Hormones are chemical substances produced by the body’s endocrine glands that help regulate various bodily functions, including the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause.
There are several types of hormonal imbalances that can affect women, including:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A condition characterised by high levels of male hormones (androgens) and an imbalance of reproductive hormones, leading to irregular periods, fertility problems, and other symptoms.
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): A group of physical and emotional symptoms that occur in the days leading up to a woman’s menstrual period.
- Menopause: A natural process that occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop producing oestrogen and progesterone, leading to the end of her reproductive years.
- Thyroid disorders: Abnormalities in the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and energy levels.

5.PCOD
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterised by the presence of multiple small cysts in the ovaries, which can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, fertility problems, and other symptoms such as weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth.
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an imbalance of hormones such as insulin, testosterone, and oestrogen. It may also be influenced by genetics, as women with a family history of PCOS are more likely to develop the condition.
In Ayurveda, the traditional medical system of India, PCOS is considered to be a result of an imbalance in the three doshas, or energies that make up the body. It is believed to be caused by an excess of the vata and kapha doshas, and an imbalance in the pitta dosha.
Treatment for PCOS in Ayurveda may involve a combination of herbs, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. Some herbs that may be used to help balance the doshas and regulate menstrual cycles include shatavari, ashwagandha, and vidari. It is important to work with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs and condition.
06.
Paediatric Problems
1.Austism
2.Hyperactive
3.Lowmemory
ETC

1.Autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication and social interaction. The exact cause of autism is not known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some research suggests that certain genetic mutations may increase the risk of autism, while environmental factors such as exposure to toxins or infections during pregnancy may also play a role.
There is no known cure for autism, and treatment often involves a combination of therapies and medications to address the specific needs and challenges of the individual with autism. These may include behavioural therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and medications to manage symptoms such as anxiety or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
In terms of Ayurveda, a traditional system of medicine from India, there is limited scientific evidence to support the use of Ayurvedic treatments for autism. While some individuals with autism and their families may find some benefit from certain Ayurvedic practices, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment. It is also important to note that some Ayurvedic treatments may have potential risks or interactions with other medications, and it is important to be cautious when considering any new treatment.

2.Hyperactive
Hyperactivity, also known as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that affects children and adults. It is characterised by a pattern of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity that interferes with daily functioning and development.
There is no known single cause of ADHD, and it is thought to be a complex condition that may be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Some potential contributing factors may include:
- Genetics: ADHD tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the disorder.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins or substances during pregnancy or early childhood may increase the risk of developing ADHD.
- Neurodevelopmental factors: ADHD may be linked to abnormal development of certain brain structures or functions, such as the neurotransmitter systems that regulate attention and behaviour.
In Ayurveda, ADHD is considered to be caused by an imbalance of the three doshas (bodily energies): vata, pitta, and kapha. Ayurvedic treatment for ADHD typically involves a combination of herbal remedies, dietary and lifestyle changes, and mind-body practices such as yoga and meditation.

1.Low memory
Low memory, or memory loss, refers to a decline in a person’s ability to remember and retain new information. It can be a normal part of the ageing process, but it can also be caused by various medical conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, brain injury, and depression.
There are several potential causes of low memory, including:
- Ageing: As people get older, their brains naturally undergo changes that can affect their ability to remember things.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and brain injury, can cause memory loss.
- Medications: Some medications, such as sedatives and certain types of blood pressure and heart medications, can cause memory loss as a side effect.
- Substance abuse: The use of drugs or alcohol can interfere with a person’s ability to remember things.
- Stress and anxiety: Chronic stress and anxiety can affect a person’s ability to remember things.
- Poor sleep: Lack of sleep can affect a person’s ability to form new memories and retain information.

07.
Anorectal Problems
1.Piles
2.Fissure
3.Fistula
ETC

1.Piles
Piles, also known as haemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the anus and lower rectum. They can be internal (inside the anus) or external (around the anus). Piles are a common condition that can cause discomfort and bleeding.
There are several potential causes of piles, including:
- Constipation: Straining to have a bowel movement can cause pressure on the veins in the anus and lead to piles.
- Diarrhoea: Loose stools can cause irritation to the anus and increase the risk of piles.
- Pregnancy: The increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic area during pregnancy can lead to the development of piles.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of piles due to the added pressure on the veins in the anus.
- Anal intercourse: This activity can cause irritation and damage to the veins in the anus, leading to piles.
- Ageing: As we age, the muscles in the anus and rectum can become weaker, which can contribute to the development of piles.
In Ayurveda, piles are known as “Arshas,” and they are classified according to their location and severity. Ayurvedic treatment for piles typically involves the use of herbal remedies and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of recurrence. Some common Ayurvedic treatments for piles include the use of herbs such as triphala and castor oil, as well as dietary changes to promote regular bowel movements and reduce constipation. It is important to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for the appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.

2.Fissure
An anal fissure is a small tear or cut in the skin lining the anus, the opening through which faeces are eliminated from the body. Fissures can be caused by a variety of factors, including constipation, diarrhoea, and straining during bowel movements. They can also be caused by childbirth, anal sex, and certain medical conditions such as Crohn’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease.
In Ayurveda, an anal fissure is considered to be caused by an imbalance of the doshas, particularly Vata and Pitta. Treatment may involve the use of herbal remedies, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications to restore balance to the doshas and promote healing. Some specific herbs that may be used to treat anal fissures in Ayurveda include amalaki, haritaki, and bibhitaki, which are used to strengthen the tissues and promote healing. Other herbs that may be used include guduchi, which has anti-inflammatory properties, and shatavari, which can help to soothe irritated tissue.
It is important to note that Ayurvedic treatment for anal fissures should be conducted under the supervision of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner. It is also important to keep in mind that while Ayurvedic treatment can be effective in some cases, it may not be suitable for everyone and may not be a substitute for traditional medical treatment.
3.Fistula
A fistula is an abnormal passage or channel that develops between two organs or vessels in the body. Fistulas can occur anywhere in the body, but they are most common in the digestive tract, urinary tract, or respiratory system. Fistulas can be caused by a number of factors, including surgery, trauma, infection, inflammation, or cancer.
In Ayurveda, fistulas are often classified according to the type of tissue involved and the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment for fistulas may involve a combination of herbal medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications to address the underlying cause and promote healing. Some herbs that may be used in the treatment of fistulas include Neem, Turmeric, and Guggulu. It is important to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for proper diagnosis and treatment of fistulas.